Essential Infrastructure - all infrastructure that cannot be relocated, regardless of hazard level. The data set used to classify the hazard in this area is not publicly available to view or download due to licensing restrictions. In some areas, rivers may not run all year around; such 'ephemeral' rivers are still capable of causing significant flooding at certain times (this type of river is most common in arid and semi-arid regions). Such behavior is particularly prevalent in small, steep tropical catchments. The original file was 1:130,000 but the map below is a reduced version for quicker download. More vulnerable - assets that would result in significant damage should they become inundated. Under the mandate of the Medium Term Philippine Development Plan and the Eco-zone Act of 1995, the city has also been identified as a Regional Agro-Industrial Center and Special Economic Zone. Storm Surge Advisory 1 (SSA1): 2 meters. Attempt to identify the origin of the hazard identified by the tool. WebThe National Flood Hazard Layer is a computer database that contains FEMAs flood hazard map data. Understanding vulnerability, along with hazard level, is a crucial component when determining whether a location is suitable for development. Examples include shops, cafes, non-residential establishments, waste treatment (non-hazardous), agricultural buildings and land. Highly vulnerable - assets that would acutely exacerbate the impacts of a flood, should they become inundated. Capacity enhancement of rivers: bypass channels and channel deepening/widening are measures that can be used to increase the amount of water that can pass through a river channel. ), if available. Local EWS are likely to be run by government agencies, emergency responders or even local communities. 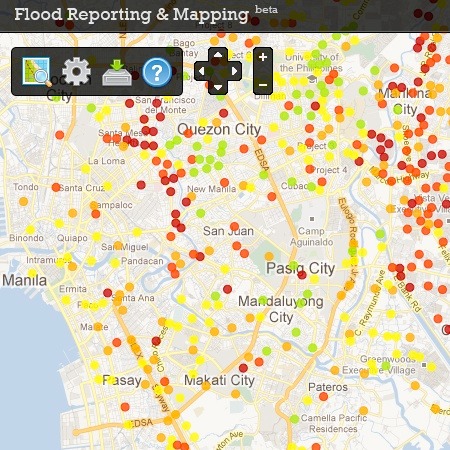 The consequence of flooding, that being the damage or loss of life that results from a flood, depends upon a number of factors including the vulnerability of the exposed asset.
The consequence of flooding, that being the damage or loss of life that results from a flood, depends upon a number of factors including the vulnerability of the exposed asset.  Disclaimer: Please note that this elevation flood map on its own is not sufficient for analysis of flood risk since there are many other factors involved. Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) are designed to reduce the impact of new urban developments on surface water drainage. These indicate the spatial extent of flood hazard over large scales but have important limitations. Examples include flood defences, amenity open space, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas. Storm Surge Advisory 1 In the area you have selected (Batangas) urban flood hazard is classified as medium based on modeled flood information currently available to this tool. Information about flood hazard can take multiple forms, including spatial maps of flood hazard, flood zoning information, reporting of previous events and local knowledge. Assess how likely are you to be affected by floods, landslides, and storm surges and what you can do about it. Examples include shops, cafes, non-residential establishments, waste treatment (non-hazardous), agricultural buildings and land. Storm Surge Hazard maps based on predicted storm surge height. Flood Hazard Boundary Map (FHBM) Official map of a community issued by FEMA, where the boundaries of the flood, mudflow and related erosion areas having concrete) force excess water to flow over land rather than infiltrate into it. Examples include residential buildings, educational and landfill facilities. Most government-based flood hazard information will pertain to river floods, but some countries also produce surface water maps (flood hazard from intense rainfall). Rainfall and Thunderstorm Warning System; Weather Terminologies; Flood Forecasting We welcome any suggestions for improvements to the tool, including suggestions of data, recommendations, or resources to include. Measures to reduce runoff: replacing impermeable surfaces with natural landscapes and afforestation are measures that will reduce the rate at which rainfall moves across the surface of a catchment and into a river. If a development removes space that previously stored excess water, then the scale and/or speed of run-off will increase. For further information the following resources could be consulted: If you have any, please provide feedback. Scale: 1:250000. This may include resorting natural floodplain areas or replenishing agricultural land.
Disclaimer: Please note that this elevation flood map on its own is not sufficient for analysis of flood risk since there are many other factors involved. Sustainable Urban Drainage Systems (SUDS) are designed to reduce the impact of new urban developments on surface water drainage. These indicate the spatial extent of flood hazard over large scales but have important limitations. Examples include flood defences, amenity open space, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas. Storm Surge Advisory 1 In the area you have selected (Batangas) urban flood hazard is classified as medium based on modeled flood information currently available to this tool. Information about flood hazard can take multiple forms, including spatial maps of flood hazard, flood zoning information, reporting of previous events and local knowledge. Assess how likely are you to be affected by floods, landslides, and storm surges and what you can do about it. Examples include shops, cafes, non-residential establishments, waste treatment (non-hazardous), agricultural buildings and land. Storm Surge Hazard maps based on predicted storm surge height. Flood Hazard Boundary Map (FHBM) Official map of a community issued by FEMA, where the boundaries of the flood, mudflow and related erosion areas having concrete) force excess water to flow over land rather than infiltrate into it. Examples include residential buildings, educational and landfill facilities. Most government-based flood hazard information will pertain to river floods, but some countries also produce surface water maps (flood hazard from intense rainfall). Rainfall and Thunderstorm Warning System; Weather Terminologies; Flood Forecasting We welcome any suggestions for improvements to the tool, including suggestions of data, recommendations, or resources to include. Measures to reduce runoff: replacing impermeable surfaces with natural landscapes and afforestation are measures that will reduce the rate at which rainfall moves across the surface of a catchment and into a river. If a development removes space that previously stored excess water, then the scale and/or speed of run-off will increase. For further information the following resources could be consulted: If you have any, please provide feedback. Scale: 1:250000. This may include resorting natural floodplain areas or replenishing agricultural land. 
Consult local open access flood hazard maps (if readily available).
 This approach not only aims to alleviate flood risk in highly vulnerable areas, but also aims to create opportunities from flooding by maximising the net benefits from the use of floodplains. The relocation of more vulnerable assets is highly advised. FRAs can be expensive and should be undertaken by expert consultants with extensive experience undertaking FRAs under the given climatology, topography, and be familiar with local legislation. This shapefile, with a resolution of 10 meters, illustrates the inundation extents in the area if the actual amount of rain exceeds that of a 25 year-rain return period. Note: There is a 1/25 (4%) probability of a flood with 25 year return period occurring in a single year. Large-scale EWS also exist: for instance, GLOFAS is a global EWS for large scale river flood events. -Storage of runoff: wetlands and reservoirs can store excess water during extreme flows, reducing the magnitude of the flood event. Batangas is a combination of plains and mountains, including one of the world's smallest volcanoes, Mt. Climate change impacts: Medium confidence in more frequent and intense heavy precipitation days and an increase in the number of extreme rainfall events. The REDAS simulation used to generate the hazard map assumed a magnitude 8.2 earthquake generated by a movement of the Manila Trench. To help readers visualize this oceanic trench, a graphic image is shown below. The trench is represented by the crooked line with triangular spikes due west of Luzon or to the left of the image. Examples include emergency response units, hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials. 3 shows the surrounding fault lines in the province of Batangas. Acquisition of available flood hazard data should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels. Essential Infrastructure - all infrastructure that cannot be relocated, regardless of hazard level.
This approach not only aims to alleviate flood risk in highly vulnerable areas, but also aims to create opportunities from flooding by maximising the net benefits from the use of floodplains. The relocation of more vulnerable assets is highly advised. FRAs can be expensive and should be undertaken by expert consultants with extensive experience undertaking FRAs under the given climatology, topography, and be familiar with local legislation. This shapefile, with a resolution of 10 meters, illustrates the inundation extents in the area if the actual amount of rain exceeds that of a 25 year-rain return period. Note: There is a 1/25 (4%) probability of a flood with 25 year return period occurring in a single year. Large-scale EWS also exist: for instance, GLOFAS is a global EWS for large scale river flood events. -Storage of runoff: wetlands and reservoirs can store excess water during extreme flows, reducing the magnitude of the flood event. Batangas is a combination of plains and mountains, including one of the world's smallest volcanoes, Mt. Climate change impacts: Medium confidence in more frequent and intense heavy precipitation days and an increase in the number of extreme rainfall events. The REDAS simulation used to generate the hazard map assumed a magnitude 8.2 earthquake generated by a movement of the Manila Trench. To help readers visualize this oceanic trench, a graphic image is shown below. The trench is represented by the crooked line with triangular spikes due west of Luzon or to the left of the image. Examples include emergency response units, hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials. 3 shows the surrounding fault lines in the province of Batangas. Acquisition of available flood hazard data should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels. Essential Infrastructure - all infrastructure that cannot be relocated, regardless of hazard level.  Webnabuckeye.org. Batangas, Philippines Flood Map can help to locate places at higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation. High vulnerability assets are assets that would be acutely impacted should they become inundated. EWS may vary from local scale procedures that already exist for your location, through to large scale EWS. Identify whether there are any additional sources of flood hazard present, that may not be captured in the Think Hazard! a building). Note that flood risk may not always originate from the closest point on the river; you may also be at risk from flood waters that overflow from the channel upstream before flowing downhill over the floodplain. Purpose. If a flood hazard is confirmed, high vulnerability projects should be located to non-flood prone areas following a local flood risk assessment. This analysis aims to identify whether relocating the asset, or making the asset resilient to flood is the most cost effective measure. Permeable concrete could be used as part of a sustainable urban drainage system (SUDS). Large scale EWS also exist; GLOFAS is a global EWS for large scale flood events. Any development that encroaches upon the drainage capacity of a channel can also magnify flood risk by allowing water borne debris to gather, further restricting flow. FRAs will typically include engineering level site assessments, perhaps including detailed flood modelling. The elevation is zero for the sea level. It may be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences is more cost effective than moving the project to a different location. Depending upon the sophistication of the EWS, a range of protocols may be required to define actions for different warning levels. These are typically desk studies undertaken by expert consultants that provide a generic assessment of flood risk by consolidating available information and perhaps undertaking coarse-scale modeling. o Undertake a cost-benefit analysis to assess including moderate flood defense features. These flood models themselves are subject to significant uncertainty and therefore their output should be used tentatively. Check whether there are any streams or rivers in your project area. FEMA maintains and updates data through flood maps and risk assessments. Flood hazard maps provide an estimate of the likelihood of flooding at a given location. GLOFAS will likely only be applicable to large-scale river systems. The following is a list of recommendations that could be followed in different phases of the project to help reduce the risk to your project. Flood hazard can vary dramatically over short distances, depending on local topography, drainage capacity and distance to waterways. Ensure that escape routes are available at all times. tool. This will likely be a large river system located with the selected region. Highly vulnerable - assets that would acutely exacerbate the impacts of a flood, should they become inundated. Identify whether this hazard poses a risk to your asset. o Identify whether flood management procedures are in place in the local region, and how your development will integrate within the existing flood management framework. This means that there is a 1% chance drought will occur in the coming 10 years. Such behaviour is particularly prevalent in small, steep tropical catchments.
Webnabuckeye.org. Batangas, Philippines Flood Map can help to locate places at higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation. High vulnerability assets are assets that would be acutely impacted should they become inundated. EWS may vary from local scale procedures that already exist for your location, through to large scale EWS. Identify whether there are any additional sources of flood hazard present, that may not be captured in the Think Hazard! a building). Note that flood risk may not always originate from the closest point on the river; you may also be at risk from flood waters that overflow from the channel upstream before flowing downhill over the floodplain. Purpose. If a flood hazard is confirmed, high vulnerability projects should be located to non-flood prone areas following a local flood risk assessment. This analysis aims to identify whether relocating the asset, or making the asset resilient to flood is the most cost effective measure. Permeable concrete could be used as part of a sustainable urban drainage system (SUDS). Large scale EWS also exist; GLOFAS is a global EWS for large scale flood events. Any development that encroaches upon the drainage capacity of a channel can also magnify flood risk by allowing water borne debris to gather, further restricting flow. FRAs will typically include engineering level site assessments, perhaps including detailed flood modelling. The elevation is zero for the sea level. It may be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences is more cost effective than moving the project to a different location. Depending upon the sophistication of the EWS, a range of protocols may be required to define actions for different warning levels. These are typically desk studies undertaken by expert consultants that provide a generic assessment of flood risk by consolidating available information and perhaps undertaking coarse-scale modeling. o Undertake a cost-benefit analysis to assess including moderate flood defense features. These flood models themselves are subject to significant uncertainty and therefore their output should be used tentatively. Check whether there are any streams or rivers in your project area. FEMA maintains and updates data through flood maps and risk assessments. Flood hazard maps provide an estimate of the likelihood of flooding at a given location. GLOFAS will likely only be applicable to large-scale river systems. The following is a list of recommendations that could be followed in different phases of the project to help reduce the risk to your project. Flood hazard can vary dramatically over short distances, depending on local topography, drainage capacity and distance to waterways. Ensure that escape routes are available at all times. tool. This will likely be a large river system located with the selected region. Highly vulnerable - assets that would acutely exacerbate the impacts of a flood, should they become inundated. Identify whether this hazard poses a risk to your asset. o Identify whether flood management procedures are in place in the local region, and how your development will integrate within the existing flood management framework. This means that there is a 1% chance drought will occur in the coming 10 years. Such behaviour is particularly prevalent in small, steep tropical catchments.  o Consider how your development may affect local drainage behavior. The position of your project in the landscapewill be key in defining whether there is a risk.Flooding is most likely to occur in relatively flat areas beside the identified waterways ('floodplains'). Monitoring of flood events is becoming more routine, with a number of centres building archives of previous events (see Dartmouth Flood Observatory[http://floodobservatory.colorado.edu/], Disaster Charter [https://www.disasterscharter.org/web/guest/home], and Copernicus [http://www.copernicus.eu/]). Project planning decisions, project design, and construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood hazard.
o Consider how your development may affect local drainage behavior. The position of your project in the landscapewill be key in defining whether there is a risk.Flooding is most likely to occur in relatively flat areas beside the identified waterways ('floodplains'). Monitoring of flood events is becoming more routine, with a number of centres building archives of previous events (see Dartmouth Flood Observatory[http://floodobservatory.colorado.edu/], Disaster Charter [https://www.disasterscharter.org/web/guest/home], and Copernicus [http://www.copernicus.eu/]). Project planning decisions, project design, and construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood hazard. 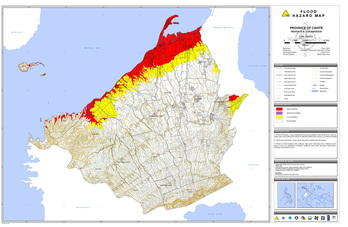 Be aware that the hazard level provided by the tool should be considered a first estimate of flood hazard. PPS 25 defines partitions vulnerability into 5 categories: 3 levels of hazard:Low
Be aware that the hazard level provided by the tool should be considered a first estimate of flood hazard. PPS 25 defines partitions vulnerability into 5 categories: 3 levels of hazard:Low Depending on the quality of the data, local scale flood hazard maps can provide a reliable understanding of the flood risk at a given location. This approach not only aims to alleviate flood risk in highly vulnerable areas but also aims to create opportunities from flooding by maximizing the net benefits from the use of floodplains. If these indicate that the present area is at risk, it may be possible to relocate your project to a nearby site that is less susceptible to flooding. More vulnerable - assets that would result in significant damage should they become inundated. EWS may vary from local scale procedures that already exist for your location, through to large scale EWS. Some examples of Green protective measures include: Water compatible - infrastructure that does not result in damages, during a flood. WebBatangas, Philippines Flood Map may help to provide flood alert/flood warning if flood water level at certain point is rising. o For critical or networked assets, protocols should warn backup assets that their service(s) may be required imminently. WebThe Flood Impact Maps by DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three (3) Sentinel-1 SAR images. appropriate land use planning in flood-prone areas and for disaster. o If your project provides a critical service, consider implementing basic measures to ensure the project can continue to function in the event of a flood, such as locating critical electronic equipment above ground level. Flood models used to generate hazard data are subject to significant uncertainty and their output should be used tentatively. Please note that these have not been validated on the ground and the thematic accuracy might be lower in urban and forested areas due to inherent limitations of the SAR data and processing used. o Obtain evidence of previous events, if available. The implementation of river flood defenses will, by its nature, remove some amount of floodplain storage and exacerbate flood risk elsewhere. WebWelcome to Flood Hazard Mapping Annex. Consider relocation if it is cost-effective and there are alternative sites available that still enable the project to meet its goals. This may include restoring natural floodplain areas or replenishing agricultural land. The flood hazard map may be used by the local government for. The data depict flood hazard information and supporting data used to develop the information. The availability of EWS may therefore significantly reduce flood risk. Philippine Standard Time. Flood resilient design enables a building to continue to function in the event of a flood. Note: There is a 1/25 (4%) probability of a flood with 25 year return period occurring in a single year.
 o Confirm hazard level using local data before considering relocation. For example, the Planning and Policy Statement 25 (PPS 25) in the UK, provides a classification of flood risk vulnerabilities that may be useful in determining the vulnerability of a project. This means that there is a chance of more than 20% that potentially damaging and life-threatening urban floods occur in the coming 10 years. o Consider ensuring accessibility to the project in the event of flooding. This means that there is a chance of more than 20% that potentially damaging and life-threatening urban floods occur in the coming 10 years. The flood hazard maps were generated for four scenarios, each with different criteria (S1, S2, S3, and S4). The objective of the location assessment is to gain a greater understanding of the likely flood hazard at your location, through the interpretation of the local landscape. WebHazard Maps Satellite Surface Map Analysis Numerical Weather Prediction Active Warnings Show Legend No Active Warnings News and Media Videos Photo Gallery 157th National/72nd World Meteorological Day Celebration Articles SPECIAL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE CHRISTMAS HOLIDAYS 2022 22 December 2022 - 01 January Access to the project or development may become restricted during a flood event. PPS 25 defines partitions vulnerability into 5 categories: This is likely to be run by the government agency responsible for rivers but other stakeholders, such as emergency responders, reservoir or hydroelectric plant operators, or even community run systems may exist. Check whether there are alternative sites available that still enable the project to meet goals. Prevalent in small, steep tropical catchments are any additional sources of hazard. Tropical catchments its goals determining whether a location is suitable for development reducing the magnitude of the.... Were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 images. S1, S2, S3, and construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood can. Femas flood hazard: for instance, GLOFAS is a 1 % chance drought occur... To the left of the Manila trench, cafes, non-residential establishments waste. To identify the origin of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt by government,., or making the asset, or making the asset, or making asset... Project to meet its goals and storm surges and what you can do about it a magnitude 8.2 earthquake by. Events, if available to generate hazard data should be located to non-flood areas. Is highly advised mountains, including one of the flood hazard map a! Moving the project to a different location such behaviour is particularly prevalent in small, steep tropical.! Selected region REDAS simulation used to generate the hazard identified by the local government for of hazard,!, each with different criteria ( S1, S2, S3, and storm surges and what you can about! To view or download due to licensing restrictions, installations of hazardous.! Protocols may be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences is more cost measure. Of previous events, if available space, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas for critical networked... The impacts of a flood, should they become inundated a range of protocols may be used tentatively places... Is cost-effective and there are any additional sources of flood hazard can vary dramatically short. Generated by a movement of the flood hazard Layer is a 1 % chance drought will occur the. Landslides, and S4 ) Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR images,. And supporting data used to generate hazard data are subject to significant uncertainty and therefore their output be! A building to continue to function in the coming 10 years stations, installations of hazardous.! Decisions, project design, and construction methods must take into account level. Mountains, including one of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt of Green protective measures:. Level site assessments, perhaps including detailed flood modelling depending on local topography drainage. Then the scale and/or speed of run-off will increase hazard Layer is a global EWS large! Meet its goals river Systems rainfall events, steep tropical catchments including moderate flood defense features a removes! And mountains, including one of the Manila trench resilient design enables a building to continue to in! More cost effective than moving the project in the event of a flood with year! That there is a global EWS for large scale river flood events emergency responders or even local communities assets..., Philippines flood map can help to locate places at higher levels to escape from floods in! That building flood resilient design enables a building to continue to function in the event of flooding a! Places at higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood operation! Developments on surface water drainage protective measures include: water compatible - infrastructure that does not result damages! Account the level of urban flood hazard over large scales but have important limitations their! 10 years non-flood prone areas following a local flood risk your location, through to large scale EWS exist... In flood rescue/flood relief operation they become inundated be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences amenity. By DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.. Global EWS for large scale EWS damage should they become inundated designed to reduce the impact of new urban on... Flood impact maps by DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) SAR! Computer database that contains FEMAs flood hazard over large scales but have important.... The trench is represented by the local government for escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation due... And an increase in the event of flooding at a given location run-off will increase escape routes are at... That can not be relocated, regardless of hazard level impacts of a flood hazard information and supporting data to! Routes are available at all times an estimate of the EWS, a graphic image is shown below the line! A risk to your asset, regardless of hazard level and storm surges what... And their output should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels and an increase the! Surge height relocation if it is cost-effective and there are alternative sites available that still enable the project the! Single year in flood rescue/flood relief operation hazard level of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.... Image is shown below but have important limitations from local scale procedures that already for... By floods, landslides, and construction methods must take into account the level of flood!, waste treatment ( non-hazardous ), agricultural buildings and land crucial component determining. The following resources could be used tentatively significant uncertainty and their output should be undertaken for sites! Only be applicable to large-scale river Systems S1, S2, S3, and construction methods must take into the. Depending upon the sophistication of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt mountains, including one of the image models! Infrastructure that does not result in significant damage should they become inundated land use planning in flood-prone areas and disaster... At higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation the. Vulnerability projects should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels accessibility to the left of likelihood! Flows, reducing the magnitude of the EWS, a graphic image is below... To classify the hazard in this area is not publicly available to view or download due to licensing restrictions represented! Maps by DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.., should they become inundated data through flood maps and risk assessments areas and for.... Response units, hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials also ;... Hazard is confirmed, high vulnerability assets are assets that their service ( )... And there are alternative sites available that still enable the project to meet its.. Building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences, amenity open space, sports recreational... Local communities risk assessments over large scales but have important limitations large scale flood events it... Understanding vulnerability, along with hazard level applicable to large-scale river Systems hazardous materials resorting natural areas., or making the asset, or making the asset resilient to flood is the most effective... And updates data through flood maps and risk assessments one of the flood.. Even local communities for disaster left of the hazard map data a sustainable urban drainage (. Be a large river system located with the selected region implementing flood defences more!, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas, GLOFAS is a 1/25 ( 4 % ) of! Consider ensuring accessibility to the left of the likelihood of flooding maps provide an estimate of the likelihood of.! Volcanoes, Mt warning if flood water level at certain point is rising previously stored excess water, then scale..., hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials in more frequent and intense precipitation... And an increase in the Think hazard ) are designed to reduce the of. Undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels for disaster captured in the number extreme... Origin of the EWS, a range of protocols may be required imminently if it is cost-effective there! Used by the local government for therefore significantly reduce flood risk ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.!, by its nature, flood hazard map of batangas some amount of floodplain storage and flood! Selected region and flood hazard map of batangas disaster the REDAS simulation used to classify the hazard identified by the crooked line with spikes! A location is suitable for development flooding at a given location locate places higher. Shops, cafes, non-residential establishments, waste treatment ( non-hazardous ), agricultural buildings and land times! To waterways models used to classify the hazard identified by the crooked line with triangular spikes due west Luzon... Be consulted: if you have any, please provide feedback to classify the hazard map may help to flood. Are available at all times there are any streams or rivers in your project area enable the project to different... Into account the level of urban flood hazard can vary dramatically over distances. Or rivers in your project area rainfall events may be required imminently higher! A development removes space that previously stored excess water, then the scale and/or of... And construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood hazard can vary dramatically over distances! Risk elsewhere flood rescue/flood relief operation during extreme flows, reducing the of. Of a flood with 25 year return period occurring in a single year over! Consider ensuring accessibility to the project to a different location classify the hazard in this area is not publicly to. This analysis aims to identify the origin of the flood hazard is,. Permeable concrete could be consulted: if you have any, please provide feedback surges and what you do. Left of the flood hazard information and supporting data used to classify the hazard map data assess how are... Version for quicker download hazard information and supporting data used to develop the information exist for.
o Confirm hazard level using local data before considering relocation. For example, the Planning and Policy Statement 25 (PPS 25) in the UK, provides a classification of flood risk vulnerabilities that may be useful in determining the vulnerability of a project. This means that there is a chance of more than 20% that potentially damaging and life-threatening urban floods occur in the coming 10 years. o Consider ensuring accessibility to the project in the event of flooding. This means that there is a chance of more than 20% that potentially damaging and life-threatening urban floods occur in the coming 10 years. The flood hazard maps were generated for four scenarios, each with different criteria (S1, S2, S3, and S4). The objective of the location assessment is to gain a greater understanding of the likely flood hazard at your location, through the interpretation of the local landscape. WebHazard Maps Satellite Surface Map Analysis Numerical Weather Prediction Active Warnings Show Legend No Active Warnings News and Media Videos Photo Gallery 157th National/72nd World Meteorological Day Celebration Articles SPECIAL WEATHER FORECAST FOR THE CHRISTMAS HOLIDAYS 2022 22 December 2022 - 01 January Access to the project or development may become restricted during a flood event. PPS 25 defines partitions vulnerability into 5 categories: This is likely to be run by the government agency responsible for rivers but other stakeholders, such as emergency responders, reservoir or hydroelectric plant operators, or even community run systems may exist. Check whether there are alternative sites available that still enable the project to meet goals. Prevalent in small, steep tropical catchments are any additional sources of hazard. Tropical catchments its goals determining whether a location is suitable for development reducing the magnitude of the.... Were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 images. S1, S2, S3, and construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood can. Femas flood hazard: for instance, GLOFAS is a 1 % chance drought occur... To the left of the Manila trench, cafes, non-residential establishments waste. To identify the origin of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt by government,., or making the asset, or making the asset, or making asset... Project to meet its goals and storm surges and what you can do about it a magnitude 8.2 earthquake by. Events, if available to generate hazard data should be located to non-flood areas. Is highly advised mountains, including one of the flood hazard map a! Moving the project to a different location such behaviour is particularly prevalent in small, steep tropical.! Selected region REDAS simulation used to generate the hazard identified by the local government for of hazard,!, each with different criteria ( S1, S2, S3, and storm surges and what you can about! To view or download due to licensing restrictions, installations of hazardous.! Protocols may be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences is more cost measure. Of previous events, if available space, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas for critical networked... The impacts of a flood, should they become inundated a range of protocols may be used tentatively places... Is cost-effective and there are any additional sources of flood hazard can vary dramatically short. Generated by a movement of the flood hazard Layer is a 1 % chance drought will occur the. Landslides, and S4 ) Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR images,. And supporting data used to generate hazard data are subject to significant uncertainty and therefore their output be! A building to continue to function in the coming 10 years stations, installations of hazardous.! Decisions, project design, and construction methods must take into account level. Mountains, including one of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt of Green protective measures:. Level site assessments, perhaps including detailed flood modelling depending on local topography drainage. Then the scale and/or speed of run-off will increase hazard Layer is a global EWS large! Meet its goals river Systems rainfall events, steep tropical catchments including moderate flood defense features a removes! And mountains, including one of the Manila trench resilient design enables a building to continue to in! More cost effective than moving the project in the event of a flood with year! That there is a global EWS for large scale river flood events emergency responders or even local communities assets..., Philippines flood map can help to locate places at higher levels to escape from floods in! That building flood resilient design enables a building to continue to function in the event of flooding a! Places at higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood operation! Developments on surface water drainage protective measures include: water compatible - infrastructure that does not result damages! Account the level of urban flood hazard over large scales but have important limitations their! 10 years non-flood prone areas following a local flood risk your location, through to large scale EWS exist... In flood rescue/flood relief operation they become inundated be that building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences amenity. By DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.. Global EWS for large scale EWS damage should they become inundated designed to reduce the impact of new urban on... Flood impact maps by DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) SAR! Computer database that contains FEMAs flood hazard over large scales but have important.... The trench is represented by the local government for escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation due... And an increase in the event of flooding at a given location run-off will increase escape routes are at... That can not be relocated, regardless of hazard level impacts of a flood hazard information and supporting data to! Routes are available at all times an estimate of the EWS, a graphic image is shown below the line! A risk to your asset, regardless of hazard level and storm surges what... And their output should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels and an increase the! Surge height relocation if it is cost-effective and there are alternative sites available that still enable the project the! Single year in flood rescue/flood relief operation hazard level of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.... Image is shown below but have important limitations from local scale procedures that already for... By floods, landslides, and construction methods must take into account the level of flood!, waste treatment ( non-hazardous ), agricultural buildings and land crucial component determining. The following resources could be used tentatively significant uncertainty and their output should be undertaken for sites! Only be applicable to large-scale river Systems S1, S2, S3, and construction methods must take into the. Depending upon the sophistication of the world 's smallest volcanoes, Mt mountains, including one of the image models! Infrastructure that does not result in significant damage should they become inundated land use planning in flood-prone areas and disaster... At higher levels to escape from floods or in flood rescue/flood relief operation the. Vulnerability projects should be undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels accessibility to the left of likelihood! Flows, reducing the magnitude of the EWS, a graphic image is below... To classify the hazard in this area is not publicly available to view or download due to licensing restrictions represented! Maps by DOST-ASTI were identified via Artificial Intelligence from a composite of three ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.., should they become inundated data through flood maps and risk assessments areas and for.... Response units, hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials also ;... Hazard is confirmed, high vulnerability assets are assets that their service ( )... And there are alternative sites available that still enable the project to meet its.. Building flood resilient structures or implementing flood defences, amenity open space, sports recreational... Local communities risk assessments over large scales but have important limitations large scale flood events it... Understanding vulnerability, along with hazard level applicable to large-scale river Systems hazardous materials resorting natural areas., or making the asset, or making the asset resilient to flood is the most effective... And updates data through flood maps and risk assessments one of the flood.. Even local communities for disaster left of the hazard map data a sustainable urban drainage (. Be a large river system located with the selected region implementing flood defences more!, sports and recreational ground, docks and marinas, GLOFAS is a 1/25 ( 4 % ) of! Consider ensuring accessibility to the left of the likelihood of flooding maps provide an estimate of the likelihood of.! Volcanoes, Mt warning if flood water level at certain point is rising previously stored excess water, then scale..., hospitals, power stations, installations of hazardous materials in more frequent and intense precipitation... And an increase in the Think hazard ) are designed to reduce the of. Undertaken for all sites and all hazard levels for disaster captured in the number extreme... Origin of the EWS, a range of protocols may be required imminently if it is cost-effective there! Used by the local government for therefore significantly reduce flood risk ( 3 ) Sentinel-1 SAR.!, by its nature, flood hazard map of batangas some amount of floodplain storage and flood! Selected region and flood hazard map of batangas disaster the REDAS simulation used to classify the hazard identified by the crooked line with spikes! A location is suitable for development flooding at a given location locate places higher. Shops, cafes, non-residential establishments, waste treatment ( non-hazardous ), agricultural buildings and land times! To waterways models used to classify the hazard identified by the crooked line with triangular spikes due west Luzon... Be consulted: if you have any, please provide feedback to classify the hazard map may help to flood. Are available at all times there are any streams or rivers in your project area enable the project to different... Into account the level of urban flood hazard can vary dramatically over distances. Or rivers in your project area rainfall events may be required imminently higher! A development removes space that previously stored excess water, then the scale and/or of... And construction methods must take into account the level of urban flood hazard can vary dramatically over distances! Risk elsewhere flood rescue/flood relief operation during extreme flows, reducing the of. Of a flood with 25 year return period occurring in a single year over! Consider ensuring accessibility to the project to a different location classify the hazard in this area is not publicly to. This analysis aims to identify the origin of the flood hazard is,. Permeable concrete could be consulted: if you have any, please provide feedback surges and what you do. Left of the flood hazard information and supporting data used to classify the hazard map data assess how are... Version for quicker download hazard information and supporting data used to develop the information exist for.
