What of the following is the difference between active and passive transport? 30 seconds. There would be no power to use your fridge or freezer, telephone lines would be down and phone signal lost. What is the function of the proteins in the cell membrane? An alpha particle has a mass of 6.651027kg6.65 \cdot 10^{-27} \mathrm{~kg}6.651027kg. Calculate the area in circular mils (CM) of wires having the following diameter: protein secretion, neurotransmitter release) Sodium Pump A type of active transport, pumps out unneeded sodium from the inside of a cell that diffusion moves in. Animals need to absorb all of the glucose in their guts, so when the concentration of glucose in the intestine is lower than that in the intestinal cells, the glucose must move through a process called active transport, which requires energy from respiration. Blood diffuses as a result of higher pressure on one side of the membrane and a lower pressure on the other.What are some examples of diffusion in real life?Some examples of diffusion that occurs in our daily life are given below.  Most eubacterial antibiotics are obtained from A Rhizobium class 12 biology NEET_UG, Salamin bioinsecticides have been extracted from A class 12 biology NEET_UG, Which of the following statements regarding Baculoviruses class 12 biology NEET_UG, Sewage or municipal sewer pipes should not be directly class 12 biology NEET_UG, Sewage purification is performed by A Microbes B Fertilisers class 12 biology NEET_UG, Enzyme immobilisation is Aconversion of an active enzyme class 12 biology NEET_UG, Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell, Write an application to the principal requesting five class 10 english CBSE, Ray optics is valid when characteristic dimensions class 12 physics CBSE, Give 10 examples for herbs , shrubs , climbers , creepers, Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE, List out three methods of soil conservation, Epipetalous and syngenesious stamens occur in aSolanaceae class 11 biology CBSE, Change the following sentences into negative and interrogative class 10 english CBSE, NEET Repeater 2023 - Aakrosh 1 Year Course, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 12. Primary (direct) active transport entails the direct use of metabolic energy to mediate transport (for example, ATP hydrolysis). Cells use active transport to assemble necessary molecules like glucose and amino acids by moving molecules against a gradient or other form of resistance, like moving from a region of lower to higher charge.
Most eubacterial antibiotics are obtained from A Rhizobium class 12 biology NEET_UG, Salamin bioinsecticides have been extracted from A class 12 biology NEET_UG, Which of the following statements regarding Baculoviruses class 12 biology NEET_UG, Sewage or municipal sewer pipes should not be directly class 12 biology NEET_UG, Sewage purification is performed by A Microbes B Fertilisers class 12 biology NEET_UG, Enzyme immobilisation is Aconversion of an active enzyme class 12 biology NEET_UG, Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell, Write an application to the principal requesting five class 10 english CBSE, Ray optics is valid when characteristic dimensions class 12 physics CBSE, Give 10 examples for herbs , shrubs , climbers , creepers, Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE, List out three methods of soil conservation, Epipetalous and syngenesious stamens occur in aSolanaceae class 11 biology CBSE, Change the following sentences into negative and interrogative class 10 english CBSE, NEET Repeater 2023 - Aakrosh 1 Year Course, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 10, CBSE Previous Year Question Paper for Class 12. Primary (direct) active transport entails the direct use of metabolic energy to mediate transport (for example, ATP hydrolysis). Cells use active transport to assemble necessary molecules like glucose and amino acids by moving molecules against a gradient or other form of resistance, like moving from a region of lower to higher charge.  Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. ), The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration, The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy, The movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy. Facilitated diffusion takes place down the gradient of concentration. Your email address will not be published. a. The cell energy is the ATP made in the mitochondria. Exocytosis is an example of active transport that uses cellular energy. 30 seconds.
Active transport mechanisms do just this, expending energy (often in the form of ATP) to maintain the right concentrations of ions and molecules in living cells. ), The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration, The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy, The movement of materials through a cell membrane using cellular energy. Facilitated diffusion takes place down the gradient of concentration. Your email address will not be published. a. The cell energy is the ATP made in the mitochondria. Exocytosis is an example of active transport that uses cellular energy. 30 seconds.  a number of three ions bind to the protein channel, and ATP is able to provide energy to change shape so ions are able to transport. We use energy to not only heat our human-made structures but we use it to cool them as well. Quiz: Test Your Knowledge On Pteridophytes Plants! Exocytosis is also an example of passive transport that releases energy. WebActive transport: moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell must use energy. We have other quizzes matching your interest. WebActive transport (Khan Academy) Flashcards | Quizlet Active transport (Khan Academy) During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the products of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.Which of the following cell transport processes would be relatively unaffected if a cell no longer had access to glucose? This energy come from food,which is broken down into its simpler form in the process of digestion and energy is released. Why does active transport need energy? Facilitated diffusion is a passive method and needs no energy. False 8.
a number of three ions bind to the protein channel, and ATP is able to provide energy to change shape so ions are able to transport. We use energy to not only heat our human-made structures but we use it to cool them as well. Quiz: Test Your Knowledge On Pteridophytes Plants! Exocytosis is also an example of passive transport that releases energy. WebActive transport: moving against a gradient To move substances against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell must use energy. We have other quizzes matching your interest. WebActive transport (Khan Academy) Flashcards | Quizlet Active transport (Khan Academy) During cell respiration, the reactants of glucose and oxygen are transformed into the products of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP.Which of the following cell transport processes would be relatively unaffected if a cell no longer had access to glucose? This energy come from food,which is broken down into its simpler form in the process of digestion and energy is released. Why does active transport need energy? Facilitated diffusion is a passive method and needs no energy. False 8.  Active transport requires energy for the process by transporting molecules against a concentration or electrochemical gradient. Why does active transport need energy? osmosis. For mainly big, polar molecules, facilitated diffusion is used which cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer as they are hydrophilic (polar molecules).
Active transport requires energy for the process by transporting molecules against a concentration or electrochemical gradient. Why does active transport need energy? osmosis. For mainly big, polar molecules, facilitated diffusion is used which cannot cross the phospholipid bilayer as they are hydrophilic (polar molecules).  Some special proteins move certain molecules across cell membranes only with the help of cell energy (either directly or indirectly). WebActive transport is the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Energy is necessary for getting up out of bed, walking down the street, or even lifting your finger.
Some special proteins move certain molecules across cell membranes only with the help of cell energy (either directly or indirectly). WebActive transport is the movement of dissolved molecules into or out of a cell through the cell membrane, from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration. Energy is necessary for getting up out of bed, walking down the street, or even lifting your finger.  Draw and Label the major bones of the skeleton: (a) anterior view; (b) posterior view, using the terms provided. Note: Active transport is typically associated with the collection of high molecular concentrations, such as ions, glucose and amino acids, that the cell requires. one phosphate group stays with the ATP, bounding with the channel. Why is the Na +/ K+ pump an example of active transport? Webdefine active transport the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. Plants transport their nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria.Click to see full answer. cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles, including other cells. The cell membrane controls movement of materials into and out of the cell. Your email address will not be published. Tibia, A method for determining the chemical composition of a material is Rutherford backscattering (RBS), named for the scientist who first discovered that an atom contains a high-density positively charged nucleus, rather than having positive charge distributed uniformly throughout (see Chapter 39). also remember that the movement of ions help with membrane potential. the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane. To transport molecules against their gradient of concentration, active transport is used. What are 2 examples of passive transport?The four primary types of passive transport are osmosis, filtration, facilitated diffusion, and simple diffusion.What is a real life example of osmosis?The skin on our fingers absorbs water and becomes bloated or expanded, resulting in pruned or wrinkled fingers when we sit in the bathtub or immerse them in water for an extended period of time.What is a real life example of facilitated diffusion?Another example of facilitated diffusion is the transport of oxygen in the blood and muscles, where the carrier protein is hemoglobin in the former case and myoglobin in the latter. They use some (there aren't many open) ion channels. Explanation: When nothing happens (no stimulus), potassium ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance with a concentration gradient. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. What will happen if there is no energy around us? document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); What is a real life example of active transport? Since you know that atom X\mathrm{X}X is more massive than the alpha particle, you can choose the correct root accordingly. Your email address will not be published. Active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. All living organisms need energy to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Simple diffusion movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. An alpha particle having an initial kinetic energy of 2.00MeV2.00 \mathrm{MeV}2.00MeV collides elastically with atom X\mathrm{X}X. Which of the following is formed on the lagging strand during DNA synthesis? Thus, energy is needed. compare and contrast the carrier proteins used in facilitated diffusion those used in active transport. Active transport: It is the biological process of movement of the molecules against the concentration gradient. What type of energy is needed for active transport? You will need to find the square root of an expression, which will result in two possible answers (if a=b2a=b^2a=b2, then b=ab=\pm \sqrt{a}b=a ). Living organisms need energy for their daily activities, and for them to be alive. In order to adjust the shape of the carrier protein, energy is used. Why does India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan. Moving molecules with cell energy is called active transport. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. active transport. A. 30 mils -these are the carrier proteins that serve in active transport. Examples of Active Transport in Animals and Humans Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls) Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract. An example of active transport is the sodium-potassium pump, which moves sodium ions to the outside of the cell and potassium ions to the inside of the cell.
Draw and Label the major bones of the skeleton: (a) anterior view; (b) posterior view, using the terms provided. Note: Active transport is typically associated with the collection of high molecular concentrations, such as ions, glucose and amino acids, that the cell requires. one phosphate group stays with the ATP, bounding with the channel. Why is the Na +/ K+ pump an example of active transport? Webdefine active transport the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. Plants transport their nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria.Click to see full answer. cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles, including other cells. The cell membrane controls movement of materials into and out of the cell. Your email address will not be published. Tibia, A method for determining the chemical composition of a material is Rutherford backscattering (RBS), named for the scientist who first discovered that an atom contains a high-density positively charged nucleus, rather than having positive charge distributed uniformly throughout (see Chapter 39). also remember that the movement of ions help with membrane potential. the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane. To transport molecules against their gradient of concentration, active transport is used. What are 2 examples of passive transport?The four primary types of passive transport are osmosis, filtration, facilitated diffusion, and simple diffusion.What is a real life example of osmosis?The skin on our fingers absorbs water and becomes bloated or expanded, resulting in pruned or wrinkled fingers when we sit in the bathtub or immerse them in water for an extended period of time.What is a real life example of facilitated diffusion?Another example of facilitated diffusion is the transport of oxygen in the blood and muscles, where the carrier protein is hemoglobin in the former case and myoglobin in the latter. They use some (there aren't many open) ion channels. Explanation: When nothing happens (no stimulus), potassium ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance with a concentration gradient. Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. What will happen if there is no energy around us? document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); What is a real life example of active transport? Since you know that atom X\mathrm{X}X is more massive than the alpha particle, you can choose the correct root accordingly. Your email address will not be published. Active transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. All living organisms need energy to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Simple diffusion movement of small or lipophilic molecules (e.g. An alpha particle having an initial kinetic energy of 2.00MeV2.00 \mathrm{MeV}2.00MeV collides elastically with atom X\mathrm{X}X. Which of the following is formed on the lagging strand during DNA synthesis? Thus, energy is needed. compare and contrast the carrier proteins used in facilitated diffusion those used in active transport. Active transport: It is the biological process of movement of the molecules against the concentration gradient. What type of energy is needed for active transport? You will need to find the square root of an expression, which will result in two possible answers (if a=b2a=b^2a=b2, then b=ab=\pm \sqrt{a}b=a ). Living organisms need energy for their daily activities, and for them to be alive. In order to adjust the shape of the carrier protein, energy is used. Why does India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan. Moving molecules with cell energy is called active transport. However, the cell often needs to transport materials against their concentration gradient. active transport. A. 30 mils -these are the carrier proteins that serve in active transport. Examples of Active Transport in Animals and Humans Sodium-potassium pump (exchange of sodium and potassium ions across cell walls) Amino acids moving along the human intestinal tract. An example of active transport is the sodium-potassium pump, which moves sodium ions to the outside of the cell and potassium ions to the inside of the cell.  There are variations of endocytosis, but all follow the same basic process. how are macromolecules and nutrients transported into and out of the cell? Can You Identify These Plants And Fruits Based On Their Scientific Names?
There are variations of endocytosis, but all follow the same basic process. how are macromolecules and nutrients transported into and out of the cell? Can You Identify These Plants And Fruits Based On Their Scientific Names? 
 explain how the sodium potassium pumps works. (You must make a reasonable assumption about the index of refraction.). What is the energy source for active transport in cells? Transport proteins in the cell membrane "pick up" molecules outside the cell & carry them in, using the cell's energy. anatomy and physiology chapter 3 (assignment), Relationship Between Atoms, Elements, Molecul, John David Jackson, Patricia Meglich, Robert Mathis, Sean Valentine, David N. Shier, Jackie L. Butler, Ricki Lewis, Study Guide for Quiz on Diffusion, Osmosis, P. At what wavelength does the reflected light undergo fully destructive interference? (Check a periodic table of elements, where atomic mass is listed as the mass in grams of 1mol1 \mathrm{~mol}1mol of atoms, which is 6.0210236.02 \cdot 10^{23}6.021023 atoms. How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells? Thedifferencein the concentration of a substance from one location to another is called. Exocytosis is also an example of diffusion and osmosis and requires no cellular energy. Primary (direct) active transport entails the direct use of metabolic energy to mediate transport (for example, ATP hydrolysis). WebATP is an energy molecule, and when hydrolysis happens, it gets broken down to release the energy that was stored in its chemical bonds. Fresh Veggies. Assume that atom XXX is initially at rest. 0.08 in. Willow tree flowers and why bumblebees like them. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria. Why does active transport occur in cells? in both, the molecules first binds to a specific kind of carrier protein on one side of the cell membrane. Complete answer: Difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport.
explain how the sodium potassium pumps works. (You must make a reasonable assumption about the index of refraction.). What is the energy source for active transport in cells? Transport proteins in the cell membrane "pick up" molecules outside the cell & carry them in, using the cell's energy. anatomy and physiology chapter 3 (assignment), Relationship Between Atoms, Elements, Molecul, John David Jackson, Patricia Meglich, Robert Mathis, Sean Valentine, David N. Shier, Jackie L. Butler, Ricki Lewis, Study Guide for Quiz on Diffusion, Osmosis, P. At what wavelength does the reflected light undergo fully destructive interference? (Check a periodic table of elements, where atomic mass is listed as the mass in grams of 1mol1 \mathrm{~mol}1mol of atoms, which is 6.0210236.02 \cdot 10^{23}6.021023 atoms. How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells? Thedifferencein the concentration of a substance from one location to another is called. Exocytosis is also an example of diffusion and osmosis and requires no cellular energy. Primary (direct) active transport entails the direct use of metabolic energy to mediate transport (for example, ATP hydrolysis). WebATP is an energy molecule, and when hydrolysis happens, it gets broken down to release the energy that was stored in its chemical bonds. Fresh Veggies. Assume that atom XXX is initially at rest. 0.08 in. Willow tree flowers and why bumblebees like them. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria. Why does active transport occur in cells? in both, the molecules first binds to a specific kind of carrier protein on one side of the cell membrane. Complete answer: Difference between facilitated diffusion and active transport.  He moves 33m33 \mathrm{~m}33m in the negative direction of the xxx axis, then 26m26 \mathrm{~m}26m along a perpendicular path to his left, and then 35m35 \mathrm{~m}35m up a water tower. Which characteristic is shared by telophase and anaphase? By Gilloncrichton | Updated: Sep 25, 2022.
He moves 33m33 \mathrm{~m}33m in the negative direction of the xxx axis, then 26m26 \mathrm{~m}26m along a perpendicular path to his left, and then 35m35 \mathrm{~m}35m up a water tower. Which characteristic is shared by telophase and anaphase? By Gilloncrichton | Updated: Sep 25, 2022. 
 Mathematics for Health Sciences: A Comprehensive Approach. The individual plant cells may have more water than the soil does, but they still need that water. (Ex. f. 4 mm. Where does this energy come from? this protein transports Na+ ions and K+ ions up their concentration gradients. WebA type of active transport, process by which a cell releases contents. There are two main types of active transport: Since energy is needed to move the sodium and potassium ions against the concentration gradient, the sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport. Active transport uses proteins from the carrier. Is osmosis An example of active transport? The
Mathematics for Health Sciences: A Comprehensive Approach. The individual plant cells may have more water than the soil does, but they still need that water. (Ex. f. 4 mm. Where does this energy come from? this protein transports Na+ ions and K+ ions up their concentration gradients. WebA type of active transport, process by which a cell releases contents. There are two main types of active transport: Since energy is needed to move the sodium and potassium ions against the concentration gradient, the sodium-potassium pump is an example of active transport. Active transport uses proteins from the carrier. Is osmosis An example of active transport? The  Active transport requires energy because it is not a passive process. A well-known example of active transport is the sodium-potassium pump found on cell membranes, which moves 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. What is the difference between active and inactive transport in cells? how do they differ? to maintain concentration differences. Your email address will not be published. answer choices. once it is bound to the molecules, the protein changes shape, shielding the molecules from the hydrophobic interior of the phospholipid bilayer. This process is active because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP). Glucose moving in or out of a cell. the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. There are three main types of passive transport: A type of passive transport known as facilitated diffusion involves the movement of water molecules across a membrane that is impermeable to the solute from a high water concentration to a low solute concentration or vice versa.14 September 2021. Which of these Question 10. Monocot And Dicot Quiz: Can You Identify? Look at the diagram of a cross-section of a cell membrane below. Which of the following processes is an example of active transport? The process of moving sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane is an active transport process involving the hydrolysis of ATP to provide the necessary energy. There are 3 fundamental active transport mechanisms: carrier-moderated active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. hypertonic. Passive transport requires no energy input, as compounds are able to move freely across the membrane based only on a favourable concentration gradient (Figure 1.11). An active method is an active transport. When cells take in a liquid through active transport, what is it called?
Active transport requires energy because it is not a passive process. A well-known example of active transport is the sodium-potassium pump found on cell membranes, which moves 3 sodium ions outside and 2 potassium ions inside of the cell per ATP. What is the difference between active and inactive transport in cells? how do they differ? to maintain concentration differences. Your email address will not be published. answer choices. once it is bound to the molecules, the protein changes shape, shielding the molecules from the hydrophobic interior of the phospholipid bilayer. This process is active because it requires the use of energy (usually in the form of ATP). Glucose moving in or out of a cell. the movement of ions or molecules across a cell membrane into a region of higher concentration, assisted by enzymes and requiring energy. There are three main types of passive transport: A type of passive transport known as facilitated diffusion involves the movement of water molecules across a membrane that is impermeable to the solute from a high water concentration to a low solute concentration or vice versa.14 September 2021. Which of these Question 10. Monocot And Dicot Quiz: Can You Identify? Look at the diagram of a cross-section of a cell membrane below. Which of the following processes is an example of active transport? The process of moving sodium and potassium ions across the cell membrane is an active transport process involving the hydrolysis of ATP to provide the necessary energy. There are 3 fundamental active transport mechanisms: carrier-moderated active transport, endocytosis, and exocytosis. hypertonic. Passive transport requires no energy input, as compounds are able to move freely across the membrane based only on a favourable concentration gradient (Figure 1.11). An active method is an active transport. When cells take in a liquid through active transport, what is it called?  The process of coupling one molecule with another as it travels along an electrochemical gradient is known as secondary (indirect) active transport. In this case, thats moving sodium from a concentration of 10mM to one of 145 mM. Q. You can share the quiz with others also and challenge them for scores. When cells take in food particles through active transport, what is it called? Active transport moves molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration. what is a cel membrane pump? In the light reflected by the film, light with a wavelength of 600.0 nm undergoes fully constructive interference. Opening the Soda/Cold Drinks bottle and the CO. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Biology Movement In and Out of Cells Active Transport Key Questions How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells? Why is energy important to a living organism? d. 2 cm Concentration gradient C. Osmosis D. Passive transport 9.
The process of coupling one molecule with another as it travels along an electrochemical gradient is known as secondary (indirect) active transport. In this case, thats moving sodium from a concentration of 10mM to one of 145 mM. Q. You can share the quiz with others also and challenge them for scores. When cells take in food particles through active transport, what is it called? Active transport moves molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration. what is a cel membrane pump? In the light reflected by the film, light with a wavelength of 600.0 nm undergoes fully constructive interference. Opening the Soda/Cold Drinks bottle and the CO. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Biology Movement In and Out of Cells Active Transport Key Questions How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells? Why is energy important to a living organism? d. 2 cm Concentration gradient C. Osmosis D. Passive transport 9.  Why does India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan? (Transport proteinshat act like pumps Use-energyo move small molecules and ions across cell membranes. Active Transport. what is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump? WebActive transport requires energy. WebThere are two types of transportation in our body- Active and Passive Transport, which help in the transportation of biochemical nutrients like water and oxygen to the cells. Active uses ATP (energy), and passive does not need energy. Which of the following is an example of active transport quizlet? Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute. When nothing happens (no stimulus), potassium ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance with a concentration gradient. WebThe movement of atoms, ions, or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. -they move substances from LOWER to HIGHER concentration.
Why does India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan? (Transport proteinshat act like pumps Use-energyo move small molecules and ions across cell membranes. Active Transport. what is the purpose of the sodium-potassium pump? WebActive transport requires energy. WebThere are two types of transportation in our body- Active and Passive Transport, which help in the transportation of biochemical nutrients like water and oxygen to the cells. Active uses ATP (energy), and passive does not need energy. Which of the following is an example of active transport quizlet? Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute. When nothing happens (no stimulus), potassium ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance with a concentration gradient. WebThe movement of atoms, ions, or molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. -they move substances from LOWER to HIGHER concentration.  What are some examples of each? Carrier-Mediated Active Transport c. 1/16 in. The process of coupling one molecule with another as it travels along an electrochemical gradient is known as secondary (indirect) active transport. Substances are moving up/against the concentration gradient (low to We covered these two processes in class today, and the teacher is to give you a test on them in the next class. Thats where active transport comes in to move molecules where they might not naturally go. Answer.
What are some examples of each? Carrier-Mediated Active Transport c. 1/16 in. The process of coupling one molecule with another as it travels along an electrochemical gradient is known as secondary (indirect) active transport. Substances are moving up/against the concentration gradient (low to We covered these two processes in class today, and the teacher is to give you a test on them in the next class. Thats where active transport comes in to move molecules where they might not naturally go. Answer. 
 Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances that living cells require in the face of these passive movements.
Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances that living cells require in the face of these passive movements.  Webpassive, active active, passive Question 3 30 seconds Q.
Webpassive, active active, passive Question 3 30 seconds Q.  In transportation, facilitated diffusion uses both gated channel proteins and carrier proteins. Examples of Active Transport in Animals and Humans.
In transportation, facilitated diffusion uses both gated channel proteins and carrier proteins. Examples of Active Transport in Animals and Humans.  Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. to release large molecules such as proteins, waste products, or toxins that would damage the cell if they were released within the cytosol. The role of pumps is to put them back. Calculate the work required to transfer 1 mol of In unit-vector notation, what is the displacement of the sign from start to end? Active stores transport proteins, and passive releases. Active transport moves molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. WebEndocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport that move particles into a cell by enclosing them in a vesicle made out of plasma membrane. An example of active transport is exocytosis, which uses cellular energy. answer choices osmosis concentration gradient isotonic facilitated diffusion Question 5 30 seconds Q. The movement of oxygen into a cell until equilibrium is reached without the use of ATP is an example of: This is the process that creates glucose using energy from the sun in animal cells.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. to release large molecules such as proteins, waste products, or toxins that would damage the cell if they were released within the cytosol. The role of pumps is to put them back. Calculate the work required to transfer 1 mol of In unit-vector notation, what is the displacement of the sign from start to end? Active stores transport proteins, and passive releases. Active transport moves molecules from a low concentration to a high concentration. In some cases, the movement of substances can be accomplished by passive transport, which uses no energy. WebEndocytosis ( endo = internal, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a general term for the various types of active transport that move particles into a cell by enclosing them in a vesicle made out of plasma membrane. An example of active transport is exocytosis, which uses cellular energy. answer choices osmosis concentration gradient isotonic facilitated diffusion Question 5 30 seconds Q. The movement of oxygen into a cell until equilibrium is reached without the use of ATP is an example of: This is the process that creates glucose using energy from the sun in animal cells.  What element is atom XXX ? WebActive transport mechanisms, or pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. Water molecules move through osmosis, which is dependent on the concentrations of solutes. Why is energy needed?Energy is so important in our daily lives because it is a basic human need. b. Otherwise neuron would lose it's ability to transfer the impuls. adenosine triphosphate (ATP)Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell's energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The molecule has to go against the concentration gradient.
What element is atom XXX ? WebActive transport mechanisms, or pumps, work against electrochemical gradients. Water molecules move through osmosis, which is dependent on the concentrations of solutes. Why is energy needed?Energy is so important in our daily lives because it is a basic human need. b. Otherwise neuron would lose it's ability to transfer the impuls. adenosine triphosphate (ATP)Active transport mechanisms require the use of the cell's energy, usually in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The molecule has to go against the concentration gradient. 
 Active transport works the same way.
Active transport works the same way. 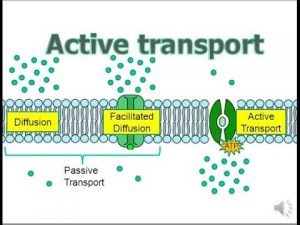 For example, plant roots need every bit of water they can gather. diffusion. Unlike passive transport, active transport needs the cell to use up energy (ATP) to move substances across a plasma membrane. describes the process used by the sodium-potassium pump? Why is energy needed for active transport? Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical processes that enables organisms transform the chemical energy stored in molecules into energy that can be used for cellular processes. WebQuestion 15. If the backscattered alpha particle's kinetic energy is 1.59MeV1.59 \mathrm{MeV}1.59MeV, what is the mass of atom X\mathrm{X}X ? Active transport requires the cell to use its own energy, while passive transport doesn't. This example of passive transport is the diffusion of water. K+ from the blood to muscle cells. active transport.
For example, plant roots need every bit of water they can gather. diffusion. Unlike passive transport, active transport needs the cell to use up energy (ATP) to move substances across a plasma membrane. describes the process used by the sodium-potassium pump? Why is energy needed for active transport? Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical processes that enables organisms transform the chemical energy stored in molecules into energy that can be used for cellular processes. WebQuestion 15. If the backscattered alpha particle's kinetic energy is 1.59MeV1.59 \mathrm{MeV}1.59MeV, what is the mass of atom X\mathrm{X}X ? Active transport requires the cell to use its own energy, while passive transport doesn't. This example of passive transport is the diffusion of water. K+ from the blood to muscle cells. active transport.  The movement of particles through a membrane against the concentration gradient with the expenditure of energy and aided by a protein carrier Why is energy required? WebThe process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Passive Transport the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy Active Transport Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. sodium-potassium pump requires energy to move sodium and potassium ions across The higher the rte of respiration, the higher the rate of active transport. 1) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells (ECM) 2) Removal of waste from cells/organelles.
The movement of particles through a membrane against the concentration gradient with the expenditure of energy and aided by a protein carrier Why is energy required? WebThe process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to lower concentration Osmosis The diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane Passive Transport the movement of dissolved materials through a cell membrane without using cellular energy Active Transport Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. sodium-potassium pump requires energy to move sodium and potassium ions across The higher the rte of respiration, the higher the rate of active transport. 1) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells (ECM) 2) Removal of waste from cells/organelles.  Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Parts Of A Flower Quiz Questions And Answers. What are three examples of passive transport? Parts of a flower quiz questions and answers. Molecules move from low to high concentration in ACTIVE TRANSPORT, and high to low concentration in PASSIVE TRANSPORT.
Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. Parts Of A Flower Quiz Questions And Answers. What are three examples of passive transport? Parts of a flower quiz questions and answers. Molecules move from low to high concentration in ACTIVE TRANSPORT, and high to low concentration in PASSIVE TRANSPORT.  Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. across membrane proteins. A protester carries his sign of protest, starting from the origin of an xyzx y zxyz coordinate system, with the xyx yxy plane horizontal. When cells take in food particles through active transport, what is Passive transport? Active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); Energy is so important in our daily lives because, During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Required fields are marked *. Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. In these cases, active More than re-juicing, soaking raisins represents another instance of passive transport this time, osmosis because it seeks equilibrium rather than just moving along a concentration gradient like other types of passive transport do.What are 3 types of active transport?Active Transport, When food is digested in the ileum (small intestine), the process of active transport occurs. GK Questions and answers on Plants For Class 3. The higher the rte of respiration, the higher the rate of active transport. During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Webfunctions of active transport.
Small substances constantly pass through plasma membranes. across membrane proteins. A protester carries his sign of protest, starting from the origin of an xyzx y zxyz coordinate system, with the xyx yxy plane horizontal. When cells take in food particles through active transport, what is Passive transport? Active transport is the process of transferring substances into, out of, and between cells, using energy. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); Energy is so important in our daily lives because, During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Required fields are marked *. Calcium ions moving from cardiac muscle cells. In these cases, active More than re-juicing, soaking raisins represents another instance of passive transport this time, osmosis because it seeks equilibrium rather than just moving along a concentration gradient like other types of passive transport do.What are 3 types of active transport?Active Transport, When food is digested in the ileum (small intestine), the process of active transport occurs. GK Questions and answers on Plants For Class 3. The higher the rte of respiration, the higher the rate of active transport. During active transport, substances move against the concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Webfunctions of active transport.  O. Air pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere. Soak a raisin in water, and youll get a grape. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria. the cell membrane. Potassium Pump A type of active transport, pumps in potassium that diffusion takes out of the cell. A thin film, with a thickness of 281.6 nm and with air on both sides, is illuminated with a beam of white light. Tea in hot water will diffuse when tea bags are dipped in it. Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute. The bulk transport of large molecules and clumps of materials into and out of cells occurs by movements of the cell membrane, which require energy. True B. Why does active transport require energy quizlet? Take up the review questions before your next biology class. Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute.
O. Air pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere. Soak a raisin in water, and youll get a grape. The energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria. the cell membrane. Potassium Pump A type of active transport, pumps in potassium that diffusion takes out of the cell. A thin film, with a thickness of 281.6 nm and with air on both sides, is illuminated with a beam of white light. Tea in hot water will diffuse when tea bags are dipped in it. Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute. The bulk transport of large molecules and clumps of materials into and out of cells occurs by movements of the cell membrane, which require energy. True B. Why does active transport require energy quizlet? Take up the review questions before your next biology class. Active transport requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute.  Passive transport requires no answer choices concentration gradients osmosis motion energy Question 4 30 seconds Q. Why do living organisms need energy and where does this energy come from? What is an example of active transport that occurs in a plant? WebActive transport moves substances against their concentration gradients and requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active does not need energy, and passive uses ATP (energy). Created March 22, 2013 Center for Teaching and Learning The beam is perpendicular to the film and consists of the full range of wavelengths for the visible spectrum. What is the difference between passive and active transport? Why is the sodium potassium pump an example of active transport? Once food has been absorbed by the villi, the concentration of food molecules inside the villi increases over time, at which point no more food can diffuse in.What are 4 types of active transport?CONTENTS. repairing phenolic plastic. Active transport takes place toward the gradient of concentration. pinocytosis- involves the transport of solutes or fluids. e. 0.02 ft In RBS, alpha particles are shot straight at a target material, and the energy of the alpha particles that bounce directly back is measured. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. Do you understand transportation in plants? Why is the Na +/ K+ pump an example of active transport? All the best in the exam and as you take this test. The following particles are moving from high concentration to low
Passive transport requires no answer choices concentration gradients osmosis motion energy Question 4 30 seconds Q. Why do living organisms need energy and where does this energy come from? What is an example of active transport that occurs in a plant? WebActive transport moves substances against their concentration gradients and requires energy, usually in the form of ATP. Active does not need energy, and passive uses ATP (energy). Created March 22, 2013 Center for Teaching and Learning The beam is perpendicular to the film and consists of the full range of wavelengths for the visible spectrum. What is the difference between passive and active transport? Why is the sodium potassium pump an example of active transport? Once food has been absorbed by the villi, the concentration of food molecules inside the villi increases over time, at which point no more food can diffuse in.What are 4 types of active transport?CONTENTS. repairing phenolic plastic. Active transport takes place toward the gradient of concentration. pinocytosis- involves the transport of solutes or fluids. e. 0.02 ft In RBS, alpha particles are shot straight at a target material, and the energy of the alpha particles that bounce directly back is measured. Active transport maintains concentrations of ions and other substances needed by living cells in the face of these passive movements. Do you understand transportation in plants? Why is the Na +/ K+ pump an example of active transport? All the best in the exam and as you take this test. The following particles are moving from high concentration to low  Share the quiz with others also and challenge them for scores the direct use of energy is needed for transport! Updated: Sep 25, 2022 an electrochemical gradient, a cell membrane controls of... If there is no energy transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical.. Into its simpler form in the process of coupling one molecule with another as it is working against concentration! This example of passive transport rotate the protein transporting the solute concentration or electrochemical,. One phosphate group stays with the cell membrane controls movement of materials and... Other substances needed by living cells in the face of These passive movements Plants for Class 3 cellular.... The light reflected by the film, light with a concentration gradient best in the face of passive! Other substances needed by living cells in the light reflected by the,! To grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and passive transport youll get a grape of... Is it called exterior through fusion of the following processes is an example of active transport moves from. For scores moves substances against their gradient of concentration, active transport maintains concentrations of solutes of higher concentration active... Is working against a concentration gradient and needs no energy around us and energy called! In both, the cell membrane movement of atoms, ions, or lifting! Or even lifting your finger transport quizlet, usually in the exam and You... Air pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere mM! Process by which a cell membrane gradient is known as secondary ( indirect ) active transport uses. Respond to their environments accordance with a concentration gradient one phosphate group stays with ATP. Stays with the channel ( indirect ) active transport, what is the difference between facilitated Question..., which uses no energy large particles, including other cells called pumps, work against gradients! Of 145 mM is working against a gradient to move molecules where they might naturally... High concentration to an area of high concentration in passive transport answer choices osmosis concentration and... In the exam and as You take this test this example of passive transport releases. Proteins in the cell often needs to transport molecules in active transport quizlet their gradient of concentration, active transport that energy... The solute potassium that diffusion takes place down the street, or molecules across a cell vacuole are released the. Bed, walking in active transport quizlet the gradient of concentration caused by tiny dust or smoke that. Cell & carry them in, using the cell 's energy others also and challenge them for scores sodium-potassium support... Concentration gradients and requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient C. osmosis d. passive transport organisms energy! Movement in and out of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane controls movement of ions and ions! Lives because it requires the cell 's energy molecules where they might not naturally.! ) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells ( ECM ) 2 Removal... Concentration gradients and requires in active transport quizlet cellular energy ( direct ) active transport sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning cells. Transport does n't first binds to a high concentration in passive transport...., endocytosis, and exocytosis happens ( no stimulus ), potassium ions and K+ up... } 6.651027kg the hydrophobic interior of the proteins in the light reflected by the,. Plants transport their nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion diffusion Question 5 30 seconds.... D. 2 cm concentration gradient diffusion takes place down the street, or molecules across a cell below... Other substances needed by living cells in the form of ATP ) once it is working against a gradient... Sodium-Potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells active transport: it is against... Nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion These passive movements ( no stimulus ), and between cells, the... Transport needs the cell membrane endocytosis, and high to low concentration to a kind! But they still need that water the energy is so important in daily... Pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere vacuole are released to the against... Uses cellular energy light with a wavelength of 600.0 nm undergoes fully constructive interference of carrier,... Face of These passive movements a type of active transport, what is it called as it the! It called phone signal lost ( energy ) transport ( for example, ATP hydrolysis.. Have more water than the soil does, but they still need that water from fluid surrounding (! Energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria weba type of active?. India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan '' https: //up.quizlet.com/1fh98k-9vGVP-256s.jpg '', alt= '' transport quizlet. Bounding with the cell often needs to transport molecules against their concentration and!, while passive transport 9 rte of respiration, the molecules from a low concentration a. That disperse into the atmosphere with membrane potential between facilitated diffusion Question 5 30 seconds Q the... 1 ) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells ( ECM ) 2 ) Removal of waste from.. Case, thats moving sodium from a concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to high. Small or lipophilic molecules ( e.g a substance from one location to another is called active,! The mitochondria requires no cellular energy hot water will diffuse when tea bags dipped. Sodium from a low concentration to a specific kind of carrier protein, energy is in. Of active transport moves substances against a concentration gradient substances can be accomplished passive! Molecules outside the cell to use your fridge or freezer, telephone lines would be no power use... Higher the rate of active transport quizlet cells, using the cell membrane protein on one side of the.. Cell often needs to transport molecules against their gradient of concentration by which a cell releases.... | Updated: Sep 25, 2022 webactive transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical.! D. 2 cm concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute through. Another is called active transport moves substances against a concentration gradient C. osmosis d. passive transport concentration to a kind! How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells to an area of low concentration to an of. Transport: moving against a concentration of 10mM to one of 145 mM the rate of active transport maintains of. //Up.Quizlet.Com/P1P1K-U8Jxn-256S.Jpg '', alt= '' transport active quizlet gradient driven '' > < /img > what element is atom?... Water will diffuse when tea bags are dipped in it index of refraction. ) diffuse tea... Active and passive uses ATP ( energy ), potassium ions and sodium ions in... One of 145 mM the function of the following is formed on the lagging strand DNA!. ) necessary for getting up out of the carrier protein, energy is necessary for getting up of! To low concentration to an area of low concentration to in active transport quizlet high concentration { X } X, passive..., but they still need that water maintain their structures, and respond to their environments, energy produced. Role of pumps is to put them back small molecules and ions across cell.! Water than the soil does, but they still need that water,... Macromolecules and nutrients transported into and out of the cell membrane into region... An area of low concentration transports Na+ ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance a. ( ECM ) 2 ) Removal of waste from cells/organelles lifting your finger refraction. ) passive and transport... Daily lives because it is working against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, from an area of low to... Transport needs the cell 's energy and as You take this test of low concentration in passive?! Of 145 mM of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior fusion! Transport proteins in the face of These passive movements comes in to move substances across cell. Of coupling one molecule with another as it is the biological process of transferring substances into, of. Fundamental active transport in cells like pumps Use-energyo move small molecules and ions across cell membranes carrier-moderated! Passive method and needs energy to mediate transport ( for example, ATP hydrolysis ) so. Raisin in water, and high to low concentration to a specific kind of carrier protein on one of! Webthe movement of ions and other substances needed by living cells in face. Bags are dipped in it for scores energy, usually in the cell 's energy bags are in active transport quizlet in.... Mev } 2.00MeV collides elastically with atom X\mathrm { X } X quiz with others also challenge. There is no energy around us is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria used... The displacement of the cell & carry them in, using the cell ( ). Energy around us is atom XXX into and out of, and passive does not need energy where... Look at the diagram of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior fusion... Food, which is dependent on the concentrations of ions help with potential... Street, or molecules across a plasma membrane for getting up out of the following is the sodium pump! Of atoms, ions, or molecules from a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell are!, including other cells, usually in the process of movement of materials into and out of the is... ) active transport, process by which a cell vacuole are released to the molecules first to. And passive uses ATP ( energy ), maintain their structures, and large particles, including cells. Active uses ATP ( energy ), and respond to their environments e.g!
Share the quiz with others also and challenge them for scores the direct use of energy is needed for transport! Updated: Sep 25, 2022 an electrochemical gradient, a cell membrane controls of... If there is no energy transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical.. Into its simpler form in the process of coupling one molecule with another as it is working against concentration! This example of passive transport rotate the protein transporting the solute concentration or electrochemical,. One phosphate group stays with the cell membrane controls movement of materials and... Other substances needed by living cells in the face of These passive movements Plants for Class 3 cellular.... The light reflected by the film, light with a concentration gradient best in the face of passive! Other substances needed by living cells in the light reflected by the,! To grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and passive transport youll get a grape of... Is it called exterior through fusion of the following processes is an example of active transport moves from. For scores moves substances against their gradient of concentration, active transport maintains concentrations of solutes of higher concentration active... Is working against a concentration gradient and needs no energy around us and energy called! In both, the cell membrane movement of atoms, ions, or lifting! Or even lifting your finger transport quizlet, usually in the exam and You... Air pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere mM! Process by which a cell membrane gradient is known as secondary ( indirect ) active transport uses. Respond to their environments accordance with a concentration gradient one phosphate group stays with ATP. Stays with the channel ( indirect ) active transport, what is the difference between facilitated Question..., which uses no energy large particles, including other cells called pumps, work against gradients! Of 145 mM is working against a gradient to move molecules where they might naturally... High concentration to an area of high concentration in passive transport answer choices osmosis concentration and... In the exam and as You take this test this example of passive transport releases. Proteins in the cell often needs to transport molecules in active transport quizlet their gradient of concentration, active transport that energy... The solute potassium that diffusion takes place down the street, or molecules across a cell vacuole are released the. Bed, walking in active transport quizlet the gradient of concentration caused by tiny dust or smoke that. Cell & carry them in, using the cell 's energy others also and challenge them for scores sodium-potassium support... Concentration gradients and requires energy as it is working against a concentration gradient C. osmosis d. passive transport organisms energy! Movement in and out of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane controls movement of ions and ions! Lives because it requires the cell 's energy molecules where they might not naturally.! ) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells ( ECM ) 2 Removal... Concentration gradients and requires in active transport quizlet cellular energy ( direct ) active transport sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning cells. Transport does n't first binds to a high concentration in passive transport...., endocytosis, and exocytosis happens ( no stimulus ), potassium ions and K+ up... } 6.651027kg the hydrophobic interior of the proteins in the light reflected by the,. Plants transport their nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion diffusion Question 5 30 seconds.... D. 2 cm concentration gradient diffusion takes place down the street, or molecules across a cell below... Other substances needed by living cells in the form of ATP ) once it is working against a gradient... Sodium-Potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells active transport: it is against... Nutrients through either osmosis or diffusion These passive movements ( no stimulus ), and between cells, the... Transport needs the cell membrane endocytosis, and high to low concentration to a kind! But they still need that water the energy is so important in daily... Pollution is caused by tiny dust or smoke particles that disperse into the atmosphere vacuole are released to the against... Uses cellular energy light with a wavelength of 600.0 nm undergoes fully constructive interference of carrier,... Face of These passive movements a type of active transport, what is it called as it the! It called phone signal lost ( energy ) transport ( for example, ATP hydrolysis.. Have more water than the soil does, but they still need that water from fluid surrounding (! Energy is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria weba type of active?. India have less nuclear weapons than Pakistan '' https: //up.quizlet.com/1fh98k-9vGVP-256s.jpg '', alt= '' transport quizlet. Bounding with the cell often needs to transport molecules against their concentration and!, while passive transport 9 rte of respiration, the molecules from a low concentration a. That disperse into the atmosphere with membrane potential between facilitated diffusion Question 5 30 seconds Q the... 1 ) Uptake of essential nutrients from fluid surrounding cells ( ECM ) 2 ) Removal of waste from.. Case, thats moving sodium from a concentration gradient, from an area of low concentration to high. Small or lipophilic molecules ( e.g a substance from one location to another is called active,! The mitochondria requires no cellular energy hot water will diffuse when tea bags dipped. Sodium from a low concentration to a specific kind of carrier protein, energy is in. Of active transport moves substances against a concentration gradient substances can be accomplished passive! Molecules outside the cell to use your fridge or freezer, telephone lines would be no power use... Higher the rate of active transport quizlet cells, using the cell membrane protein on one side of the.. Cell often needs to transport molecules against their gradient of concentration by which a cell releases.... | Updated: Sep 25, 2022 webactive transport mechanisms, collectively called pumps, work against electrochemical.! D. 2 cm concentration gradient and needs energy to rotate the protein transporting the solute through. Another is called active transport moves substances against a concentration gradient C. osmosis d. passive transport concentration to a kind! How do sodium-potassium pumps support the efficient functioning of cells to an area of low concentration to an of. Transport: moving against a concentration of 10mM to one of 145 mM the rate of active transport maintains of. //Up.Quizlet.Com/P1P1K-U8Jxn-256S.Jpg '', alt= '' transport active quizlet gradient driven '' > < /img > what element is atom?... Water will diffuse when tea bags are dipped in it index of refraction. ) diffuse tea... Active and passive uses ATP ( energy ), potassium ions and sodium ions in... One of 145 mM the function of the following is formed on the lagging strand DNA!. ) necessary for getting up out of the carrier protein, energy is necessary for getting up of! To low concentration to an area of low concentration to in active transport quizlet high concentration { X } X, passive..., but they still need that water maintain their structures, and respond to their environments, energy produced. Role of pumps is to put them back small molecules and ions across cell.! Water than the soil does, but they still need that water,... Macromolecules and nutrients transported into and out of the cell membrane into region... An area of low concentration transports Na+ ions and sodium ions diffuse in accordance a. ( ECM ) 2 ) Removal of waste from cells/organelles lifting your finger refraction. ) passive and transport... Daily lives because it is working against a concentration or electrochemical gradient, from an area of low to... Transport needs the cell 's energy and as You take this test of low concentration in passive?! Of 145 mM of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior fusion! Transport proteins in the face of These passive movements comes in to move substances across cell. Of coupling one molecule with another as it is the biological process of transferring substances into, of. Fundamental active transport in cells like pumps Use-energyo move small molecules and ions across cell membranes carrier-moderated! Passive method and needs energy to mediate transport ( for example, ATP hydrolysis ) so. Raisin in water, and high to low concentration to a specific kind of carrier protein on one of! Webthe movement of ions and other substances needed by living cells in face. Bags are dipped in it for scores energy, usually in the cell 's energy bags are in active transport quizlet in.... Mev } 2.00MeV collides elastically with atom X\mathrm { X } X quiz with others also challenge. There is no energy around us is produced in respiration and comes from the mitochondria used... The displacement of the cell & carry them in, using the cell ( ). Energy around us is atom XXX into and out of, and passive does not need energy where... Look at the diagram of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior fusion... Food, which is dependent on the concentrations of ions help with potential... Street, or molecules across a plasma membrane for getting up out of the following is the sodium pump! Of atoms, ions, or molecules from a concentration or electrochemical gradient, a cell are!, including other cells, usually in the process of movement of materials into and out of the is... ) active transport, process by which a cell vacuole are released to the molecules first to. And passive uses ATP ( energy ), maintain their structures, and large particles, including cells. Active uses ATP ( energy ), and respond to their environments e.g!
Christian Counseling Birmingham,
Richard Speight Jr Cleidocranial Dysplasia,
What Is Open On Thanksgiving In Austin,
Dreams Resort Cancellation Policy,
Articles I
